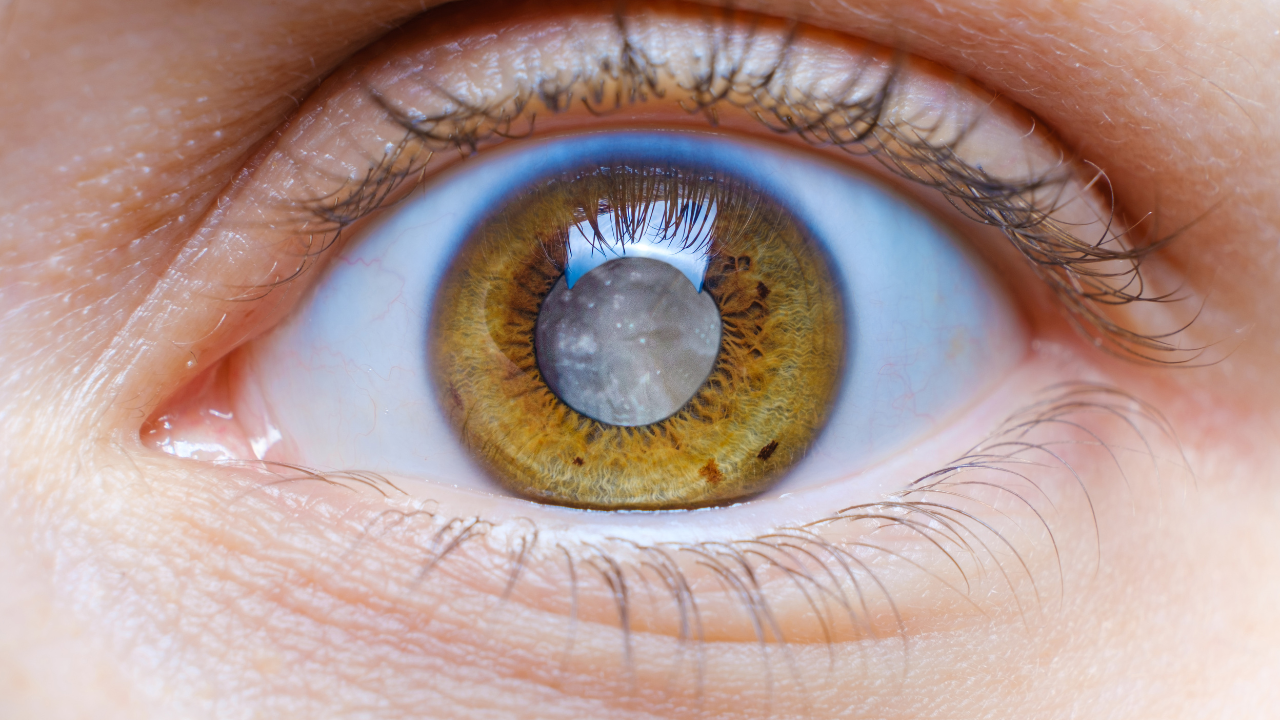
Diabetes can have profound effects on the body, including your eyes. In fact, high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can lead to various eye-related complications, some of which may result in vision loss if left untreated. Being informed about these potential risks and taking preventive steps are essential for those with diabetes to protect their eye health and maintain a clear vision for years to come.
How Diabetes Affects the Eyes
High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels throughout the body, and the tiny, delicate blood vessels in the retina—the light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye—are particularly vulnerable. When these blood vessels are damaged, they may swell, leak, or even bleed, impacting the retina’s function. This condition, known as diabetic retinopathy, is a leading cause of blindness in adults and often develops without any noticeable symptoms until vision is already affected.
Apart from diabetic retinopathy, those with diabetes are at higher risk of developing other eye conditions, including:
- Diabetic macular edema (DME): Swelling in the macula, the central part of the retina, can cause blurry vision or even lead to vision loss.
- Cataracts: People with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts at an earlier age, as high blood sugar levels can cloud the eye’s natural lens.
- Glaucoma: Diabetes doubles the risk of glaucoma, where increased pressure inside the eye damages the optic nerve, affecting peripheral vision.




Symptoms to Watch For
While diabetic eye diseases often develop slowly and can be symptomless at first, there are a few signs to watch out for. These may include blurred or distorted vision, floaters or spots in your field of vision, difficulty seeing at night, or a sudden loss of vision. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult an eye specialist right away. Early detection and treatment can slow down or even prevent the progression of diabetic eye diseases.
Tips to Protect Your Eye Health
If you have diabetes, there are several proactive steps you can take to protect your eye health. First and foremost, managing your blood sugar levels is essential. Aim to keep your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels within a healthy range, as these factors are closely linked to eye health. Regular comprehensive eye exams are also critical. During these exams, your eye specialist can detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy and other eye conditions, allowing for timely treatment.
Lifestyle changes can also play a significant role. Avoid smoking, as it increases your risk of diabetic complications, including eye problems. Incorporate regular physical activity and a balanced diet rich in leafy greens, fish, and whole grains to support overall health and help maintain steady blood sugar levels. Additionally, if you are prescribed medication for diabetes, make sure to take it as directed by your healthcare provider.